Lung Cancer and Treatment: Comprehensive Insights for Patients
Lung cancer remains one of the most challenging illnesses in the world, with significant implications for patient health, treatment protocols, and survival rates. Understanding lung cancer and its treatment options is paramount for patients, families, and caregivers. This comprehensive article aims to elucidate the various facets of lung cancer, ensuring that readers have access to the most relevant and insightful information available.
Understanding Lung Cancer
Lung cancer occurs when abnormal cells in one or both lungs grow uncontrollably, forming tumors. It is predominantly categorized into two types:
- Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) - This is the most prevalent type, accounting for approximately 85% of all lung cancer cases. NSCLC has several subtypes, including adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma.
- Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) - This type is less common but tends to grow and spread more quickly compared to NSCLC. It is often associated with significant smoking history.
Symptoms of Lung Cancer
Identifying the symptoms of lung cancer early can be crucial for effective treatment. Common symptoms to be aware of include:
- Persistent Cough: A cough that does not go away or worsens over time.
- Chest Pain: Pain or discomfort in the chest that may feel worse with deep breathing.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing or feeling winded during daily activities.
- Wheezing: A whistling sound when you breathe.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Losing weight without trying can be a red flag.
- Coughing Up Blood: Even small amounts of blood can indicate a serious condition.
Risk Factors Associated with Lung Cancer
Several factors increase the risk of developing lung cancer, including:
- Smoking: The primary risk factor, responsible for approximately 85% of lung cancer cases.
- Secondhand Smoke: Exposure to smoke from others can also increase risk.
- Radon Exposure: This naturally occurring gas can accumulate in homes and is the second leading cause of lung cancer.
- Occupational Hazards: Certain jobs expose workers to carcinogens such as asbestos, arsenic, and diesel exhaust.
- Family History: A genetic predisposition to lung cancer may be a risk factor, especially in non-smokers.
Diagnosis of Lung Cancer
Early diagnosis is critical in improving the prognosis of lung cancer patients. The following methods are commonly utilized to diagnose this condition:
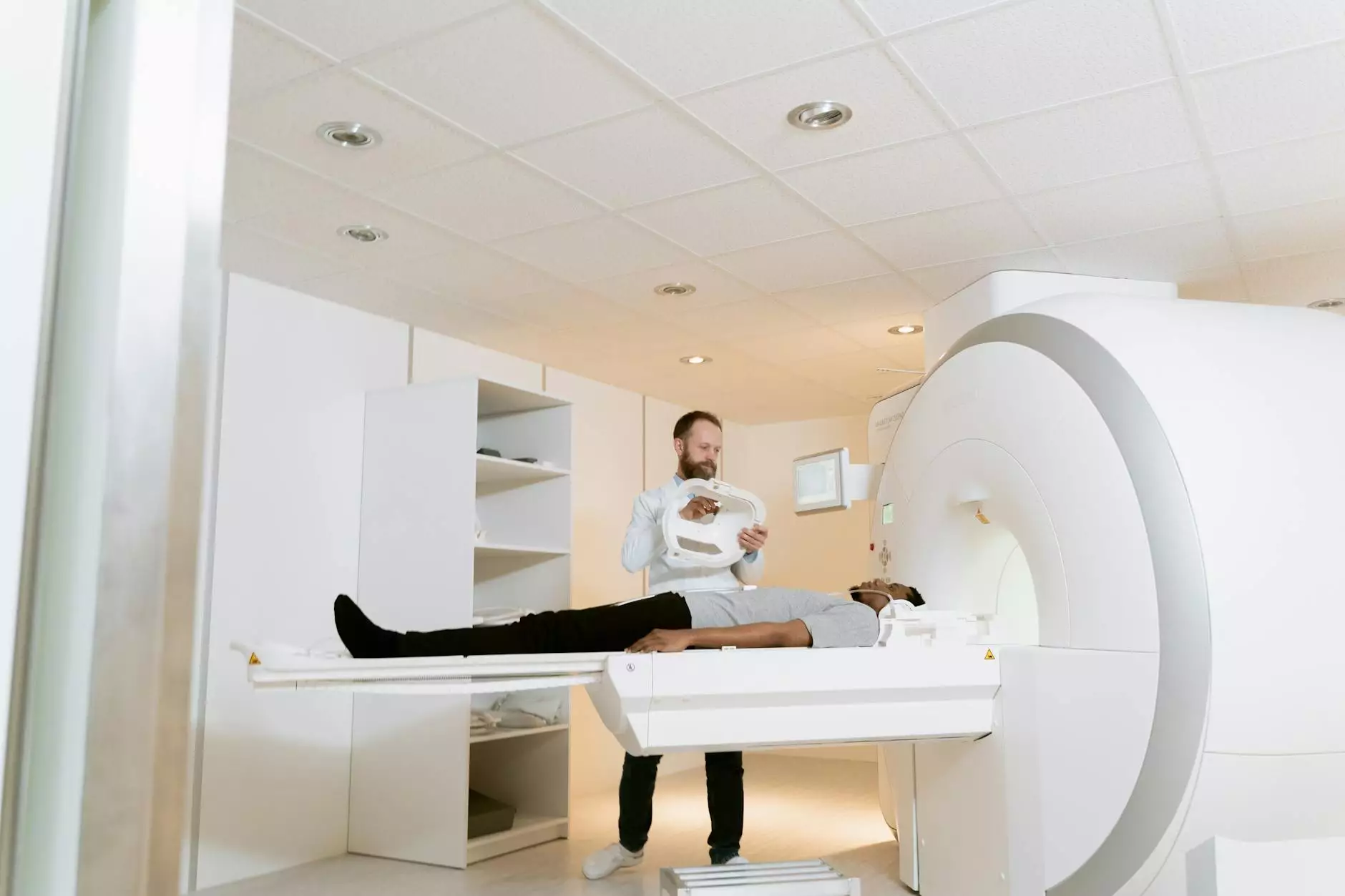
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs help visualize abnormalities in the lungs.
- Sputum Cytology: Examining mucus from the lungs can reveal cancer cells.
- Biopsy: A definitive diagnosis is often made by obtaining a tissue sample through a bronchoscopy or needle biopsy.
Lung Cancer Staging
Staging is essential to determining the extent of lung cancer and the most effective treatment options available. The most commonly used system is the TNM system, which assesses:
- T (Tumor): The size and extent of the primary tumor.
- N (Node): The number of nearby lymph nodes that are affected.
- M (Metastasis): Whether the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
Treatment Options for Lung Cancer
Upon diagnosis, patients will discuss treatment options with their healthcare providers, which may include:
1. Surgery
Surgery is often the best option for early-stage lung cancer. Types of lung cancer surgery include:
- Lobectomy: Removal of a lobe of the lung.
- Pneumonectomy: Complete removal of one lung.
- Sleeve Resection: Removal of a portion of a bronchus along with the tumor.
2. Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy utilizes high-energy waves to target and kill cancer cells. It's often used as:
- A primary treatment for those who cannot undergo surgery.
- An adjuvant treatment post-surgery to eliminate residual cancer cells.
- A palliative measure to relieve symptoms in advanced cases.
3. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy employs cytotoxic drugs to target rapidly dividing cancer cells. It may be used before surgery (neoadjuvant therapy) or after (adjuvant therapy) and is sometimes the main treatment for advanced cancers.
4. Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapies are designed to attack specific characteristics of cancer cells, such as:
- EGFR Inhibitors: Such as erlotinib or gefitinib.
- ALK Inhibitors: Such as crizotinib.
- MEK Inhibitors: Targeting certain pathways in cancer growth.
5. Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy helps the body's immune system recognize and attack cancer cells. Drugs, like pembrolizumab, have shown promise in treating lung cancer, particularly in advanced stages.
Living with Lung Cancer
Receiving a lung cancer diagnosis is overwhelming. It is vital for patients to seek emotional and psychological support to cope with the challenges ahead. Helpful strategies include:
- Joining Support Groups: Connecting with others facing similar challenges can alleviate feelings of isolation.
- Counseling: Professional therapists can provide coping strategies to manage anxiety and depression.
- Nutrition and Exercise: Maintaining a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity can enhance overall well-being and combat fatigue.
Conclusion
Understanding lung cancer and treatment options is essential for patients and caregivers alike. Continuous advancements in research and treatment methodologies offer hope for improved outcomes and enhanced quality of life for those affected by this disease. At neumarksurgery.com, we are committed to providing comprehensive care and support to all our patients. It is crucial to engage in open discussions with healthcare professionals to choose the most appropriate treatment pathway tailored to individual needs.